Gear pitch is key in gear systems, affecting how well machines work. It’s important to know about gear pitch and how to calculate it. This knowledge helps in making gear systems better.
Gear pitch is about the space between gear teeth. It changes how fast and strong a machine can be. Getting gear pitch right is vital for gears to work well together and move power smoothly.
Learning about gear pitch is essential for top-notch gear systems. Knowing how to calculate it helps engineers make better gear systems. This is important in many fields, like cars and planes.
What Is Gear Pitch and Why It Matters
Gear pitch is key to a machine’s performance and efficiency. It’s about how gears work together. Simply put, it’s the space between a gear’s teeth. This space is vital for a machine’s speed and torque.
The role of gear pitch is wide-ranging. It impacts a machine’s speed, efficiency, and reliability. The right gear pitch ensures gears fit together well, reducing wear. But the wrong one can lower performance, increase energy use, and even cause machine failure.
Definition of Gear Pitch
The gear pitch definition is based on the circular pitch. This is the space between two teeth on a gear. It’s usually measured in inches or millimeters. Knowing this helps find the right gear ratio for a machine.
The Role of Pitch in Gear Systems
The gear pitch is essential in gear systems. It sets the speed and torque of a machine, and its efficiency and reliability. A correct gear pitch means gears mesh well, reducing wear.
Impact on Machine Performance
The gear pitch greatly affects a machine’s performance. The wrong pitch can lower performance, increase energy use, and even cause failure. But the right pitch boosts efficiency and reliability, cutting down on maintenance and downtime.
Knowing about gear pitch is vital for making efficient and reliable machines. By picking the right gear pitch, engineers and manufacturers can make machines work better. This saves costs and boosts productivity.
| Gear Pitch | Definition | Role | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Pitch | Distance between teeth | Determines speed and torque | Affects machine performance |
| Diametral Pitch | Number of teeth per inch | Affects gear ratio | Influences machine efficiency |
Types of Gear Pitch Measurements
Gear pitch measurements are key to a gear system’s performance and efficiency. There are several types, like diametral pitch, circular pitch, and module. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks, depending on the application.
Some common gear pitch types include:
- Diametral pitch: This is the most common type. It’s the number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter.
- Circular pitch: Used for gears with a circular pitch. It’s the distance between two adjacent teeth.
- Module: A metric measurement for gear size. It’s the pitch diameter divided by the number of teeth.
Knowing the different gear pitch measurements is vital for designing and making efficient gear systems. Here’s a table that summarizes the main types:
| Type of Measurement | Definition | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diametral Pitch | Number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter | Easy to calculate, widely used | Not suitable for gears with complex tooth profiles |
| Circular Pitch | Distance between two adjacent teeth | Accurate for gears with circular pitch | Not suitable for gears with non-circular pitch |
| Module | Pitch diameter divided by the number of teeth | Metric measurement, easy to use | Not widely used in some industries |
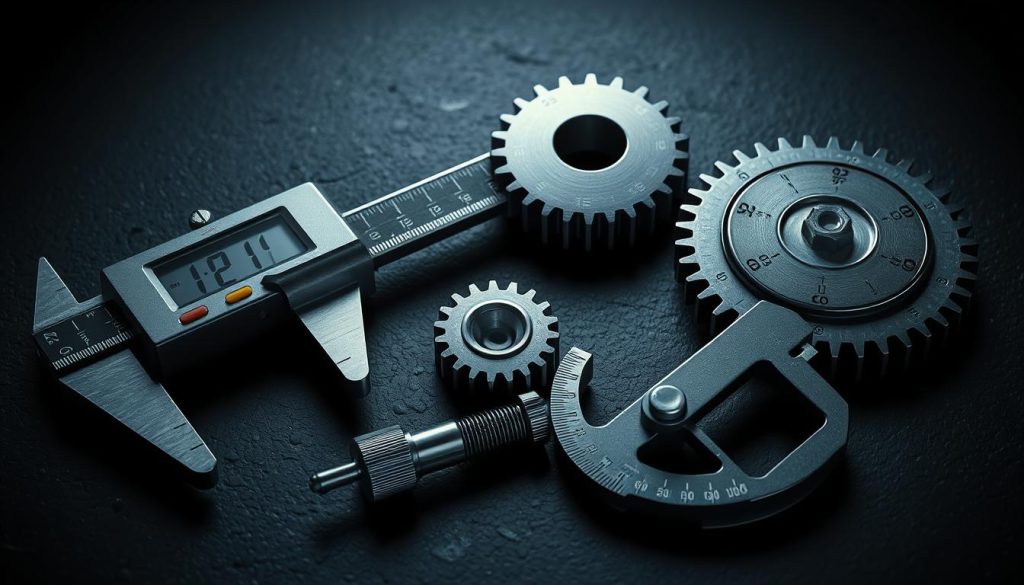

Calculating and Measuring Gear Pitch
To make sure gear systems work right, it’s key to get the gear pitch calculation just right. This means figuring out the tooth size and spacing. It’s a complex task that looks at many factors, like the gear type and its use.
There are a few ways to figure out gear pitch, like the diametral pitch method or the circular pitch method. The right method depends on the gear system’s needs and the tools you have. Gear pitch measurement tools are vital for getting the calculation right and spotting any issues with the teeth.
Tools like calipers, micrometers, and gear pitch gauges are common for measuring gear teeth. They help find any problems with the teeth’s size or spacing. With these tools and the right methods, engineers and makers can make sure their gear systems run smoothly.
Here are some important things to think about for gear pitch calculation and measurement:
- Getting the tooth size and spacing right
- Picking the best calculation method
- Using precise gear pitch measurement tools
- Checking and keeping gear systems in good shape
By sticking to these tips and using the right tools and methods, engineers and makers can make sure their gear systems work their best. This reduces mistakes and boosts performance.
Common Gear Pitch Standards and Specifications
Gear pitch standards and specifications are key for gear system compatibility and performance. The American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) set these standards. They guide gear pitch specifications, like diametral pitch, circular pitch, and tooth thickness.
It’s vital for manufacturers and engineers to know these standards. They need to design gear systems that meet specific needs. Following these standards helps avoid mistakes and reduces gear failure risks.
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries have their own gear pitch standards and specs. For example, the aerospace industry needs gears that are durable and reliable. Here are some industry-specific requirements:
| Industry | Gear Pitch Standard | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | AGMA 2005 | Diametral pitch: 10-20 |
| Automotive | ISO 1328 | Circular pitch: 10-30 mm |
| Industrial | AGMA 2015 | Tooth thickness: 1-5 mm |
By sticking to gear pitch standards, manufacturers can make sure their gear systems work well and safely. This is very important in industries where gear failure can cause big problems.
Troubleshooting Gear Pitch Problems
Fixing gear pitch issues is key for machines to work well. Problems with gear pitch can cause machines to run less efficiently. They can also lead to more wear and tear, and even break down completely.
To solve gear pitch problems, it’s important to know what causes them. Common issues include wrong gear pitch measurements or teeth that are worn out.
Fixing gear pitch problems means following a step-by-step plan. This includes checking the gear teeth for wear, measuring the gear pitch, and looking at how the machine is performing. By doing this, manufacturers can find and fix problems fast. This saves time and money on repairs.
Signs of gear pitch problems include strange noises, vibrations, or overheating. To fix these, manufacturers can try a few things. For example:
- Adjusting the gear pitch measurements to ensure accurate alignment
- Replacing worn-out gear teeth or components
- Implementing regular maintenance schedules to prevent future issues
Understanding why gear pitch problems happen and using good troubleshooting methods helps machines run better. It also saves money and boosts efficiency. Keeping an eye on gear pitch systems and doing regular maintenance can stop problems before they start. This keeps machines running smoothly and prevents breakdowns.
Conclusion: Mastering Gear Pitch for Optimal Performance
In the complex world of gear systems, mastering gear pitch is key to unlocking optimal performance. We’ve covered the details of gear pitch, how to measure it, and the standards that guide its use. Knowing the importance of gear pitch helps engineers and technicians make sure their equipment works at its best.
Whether you’re working with diametral pitch calculations or circular pitch measurements, being able to accurately assess and fix gear pitch issues is vital. Keeping up with the latest standards and best practices helps professionals stay ahead and deliver top-notch results.
As we wrap up our exploration of gear pitch, remember that learning and paying attention to detail are essential. By applying the principles from this article, you’ll be on your way to optimal performance. You’ll also gain a deeper understanding of the critical role gear pitch plays in mechanical systems.





